Prevent Foodborne Illness: ANSP Warns
Nineteen individuals in Chișinău, ranging in age from 8 to 48, have sought medical attention after experiencing symptoms consistent with foodborne toxiinfection.
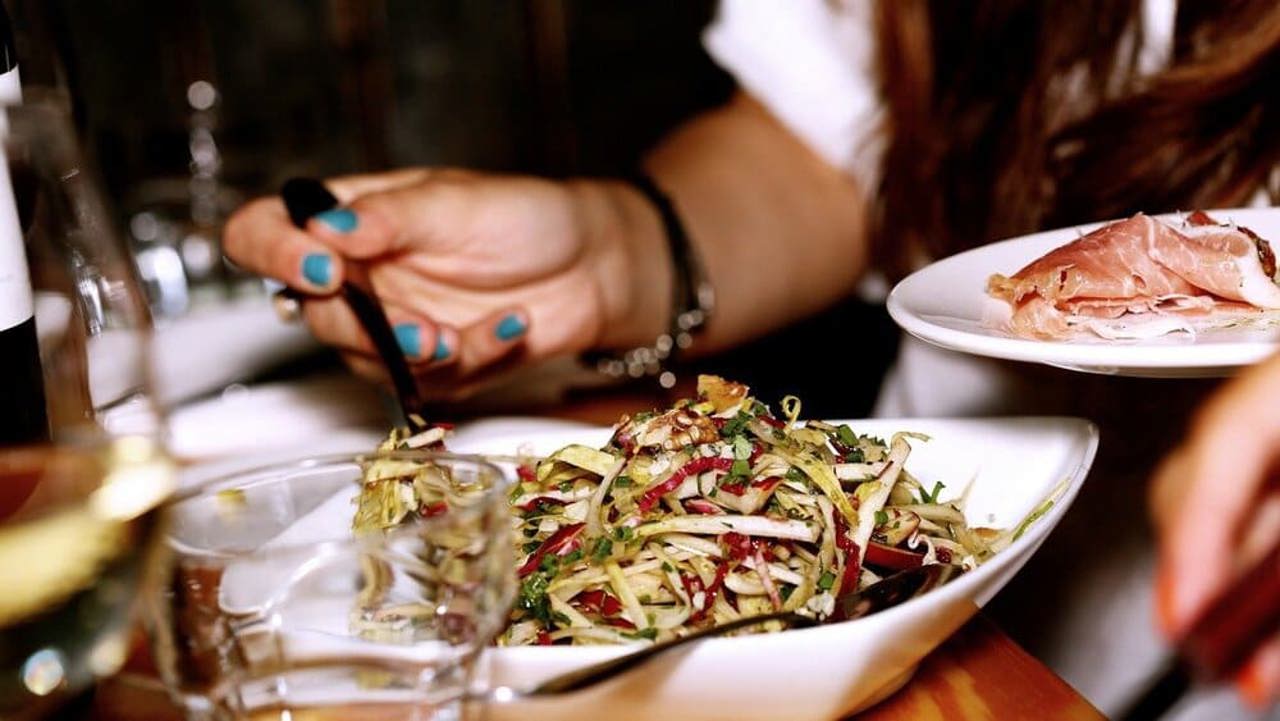

Thus far, eight patients have been hospitalized, while the remaining individuals are receiving outpatient care, according to the National Agency for Public Health (ANSP).
Upon admission, patients exhibited a combination of general weakness, fever ranging from 38 to 40 degrees Celsius, chills, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and frequent loose stools. The severity of illness in these individuals has been classified as moderate to serious. Laboratory tests conducted on biological samples from both the affected patients and employees of the implicated food service establishment identified Salmonella enteritidis.
ANSP emphasizes that salmonellosis is a prevalent bacterial infection affecting both humans and animals, specifically targeting the intestinal tract. The most common route of transmission for humans is the consumption of contaminated and undercooked meat, eggs, or egg-based products (such as mayonnaise).
Furthermore, secondary contamination of food products can occur when individuals carrying the Salmonella bacteria are involved in food preparation. To mitigate the risk of acute diarrhoeal diseases and foodborne toxiinfections, ANSP urges the public to adhere to several essential guidelines. These include frequent handwashing with soap after using the restroom and before meals, maintaining proper separation of cooked and raw food items within refrigerators, and ensuring that all food products undergo thorough cooking.
Two additional crucial practices involve storing prepared food items under refrigeration and utilizing water and raw ingredients from safe sources during food preparation.
Translation by Iurie Tataru